Manoil Lab
MUTANT DISTRIBUTION IS BEING DISCONTINUED. Individual mutant and pooled mutant library distribution will end October 15, 2022 and we will stop accepting new orders September 15, 2022. We will continue to distribute our few remaining complete single mutant arrayed libraries for P. aeruginosa, A. baumannii and K. pneumoniae until December 15, 2022 or until our copies of them are exhausted.
Acinetobacter baumannii AB5075 Mutant Library
Individual strains, transposon mutant pools, and copies of the Acinetobacter baumannii Three-Allele Transposon Mutant Library are available for a charge to the research community through a nonprofit cost center at the University of Washington. There are two to three mutants available for most nonessential genes. The strains have been single colony-purified, and the insertion locations for most of them have been confirmed by re-sequencing. Individual mutants are available, as is the parent strain (AB5075-UW). In-depth information about the library can be found in: Gallagher et al. 2015, J. Bacteriol. 197:2027
Requesting individual mutants
The library Excel file (which can be downloaded from the link below) details information about each mutant in the three-allele library. Most of the column headings are self-explanatory. There is also a description of column headings on the second sheet of the Excel file (“Legend”).
To request individual mutants, fill out the order form that corresponds to your type of institution (academic or nonacademic; links below) and send the completed Excel order form to abmutant [ at ] uw.edu. There is an instruction sheet in the order form file, but please let us know if you have any questions about the form itself, the mutants, or the ordering process.
For requests from countries requiring import or other permits, the requestor must obtain the necessary permits and email copies to abmutant [ a t ] uw.edu. All charges resulting from failure to provide the required permits will be paid by the requestor, including the cost of return shipment following customs rejection. While email is preferred, if it is necessary to fax copies of permits, they may be faxed to Manoil lab at +1-206-685-7301.
We are able to accept payment by purchase order number, check, bank transfer, or credit card for smaller orders. Credit card payments may be made via a secure website; the link to the website will be provided with the invoice. We require a purchase order to be emailed with the order form for orders exceeding $1,000.
Choice of strains
In creating a large arrayed mutant library like this one, it is inevitable that some assignments will fail to check out. We have done our best to minimize cross-contamination and insertion mis-assignment by colony purification and two rounds of sequencing. In quality control tests of the three-allele library, a small percentage of mutant insertion sites did not match the original assignments. In addition, high throughput growth and distribution may lead to some mixed cultures.
We have included multiple independent insertion mutants for most genes, and suggest that multiple mutants corresponding to genes of interest be requested to help provide coverage in case individual mutants cannot be confirmed. Unfortunately, we are unable to provide replacements for mutants that cannot be confirmed. We also recommend using the parent to this library (AB5075-UW) for comparisons.
Receipt and maintenance of strains
Individual strains are sent as stab cultures in semisolid agar. Samples of the strains received should be maintained as frozen stocks (–80°C) in the recipient laboratory. We recommend that the researcher streak from the stab onto a nutrient medium such as LB agar (without antibiotic) immediately after receipt. After overnight growth scoop up a generous sample from the dense part of the streak for the frozen stock (in LB containing 5% DMSO or 20% glycerol).
Quality control is performed to ensure that you are sent a viable stock. It is possible that a strain you requested is viable for only a short period of time due to the mutation it harbors, and would not be recoverable after shipping. Once a strain has been shipped and is at that time viable, there will be no refunds or reshipment without an additional order.
Confirmation of Strains
We urge investigators to check the identities of mutants by PCR or sequencing prior to use, and to share this information with us for incorporation into the strain database. We recommend you test 10 individual colonies by PCR both with flanking primers and with a transposon-specific primer paired with a flanking primer to confirm your mutants.
For each gene of interest, the researcher should design appropriate flanking primers. These primers should be initially tested using the wild type parent strain. To show that the intact gene is absent in the insertion strain, PCR with the same primers should yield either no band or a band corresponding to a much larger product.
To show the presence of the transposon insertion, use a transposon-specific primer with one of the flanking primers. For transposon T26, we recommend transposon-specific primer Pgro-172 (5’-TGAGCTTTTTAGCTCGACTAATCCAT-3'); for transposon T101, use transposon-specific primer hyg-174 (5’-GAAGCATTTATCAGGGTTATTGTCTCA-3’). The flanking primer should be chosen according to the orientation of the transposon relative to the insertion site. For ‘F’ (forward) insertions, the transposon-specific primer will point back toward lower genome positions.
On occasion, purified transposon mutant strains produce both wild-type and insertion mutant bands in the PCRs described above. We suspect these are usually bacteria carrying both wild-type and insertion mutant alleles and arise from transposon insertion in one copy of a tandem duplication that includes the gene of interest. Such strains are frequently found for essential genes in which wild-type function is required for viability.
When you have either positively or negatively confirmed a mutant strain, please send an email reporting your results to abmutant [at] uw.edu.
Phase variation in library strains.
Please note that Phil Rather's group has described a phase variation in A. baumannii AB5075 that affects colony morphology and other phenotypes (Tipton et al, J. Bacteriol. 197, 2593-2599 (2015)). Mutants from our three-allele library exhibit the variation, and it is important where feasible to employ strains of the same colony type when comparing phenotypes. Conditions for distinguishing colony types are described in the Tipton et al. publication.
Pooled Transposon Mutant Library
The transposon mutant pools of AB5075 were created by transformation of transposon-transposase complexes of tetracycline resistance transposon T26 and consist of approximately 450,000 insertion mutants. Pools come in 1-mL aliquots stored at –80ºC in 10% glycerol. See Gallagher et al. (2015) Resources for genetic and genomic analysis of emerging pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Bacteriol. 197:2027. doi:10.1128/mBio.01655-17
As with purchases of individual mutants, we require a purchase order to be emailed with the order form for orders exceeding $1,000.
Ordering complete arrayed library copies and pooled libraries
In making replicates of the entire library for distribution, several steps of quality control are performed. Strains are assessed for their growth by visual assessment of turbidity and strains that did not grow well are grown up individually and included in supplemental plates. Sanger sequencing is performed on a subset of wells (~3% of the library) to ensure plate orientation and library integrity (typically <2% of mutants provide unexpected sequence).
Library and pool orders may be initiated either by contacting us at abmutant [at] uw.edu or by filling out the Excel order form (instructions are on the first sheet) and emailing the form to abmutant [at] uw.edu.
Please contact us with any questions about these products and the ordering process.
Mutant naming
In publications, please reference strains from the Three-allele Library by Strain Name (unique identifier) and refer to the genotype in the following way: gene name (or ABUW Locus if there is no gene name)-well name (final three digits of the location field) as the allele number::Transposon name (T26 or T101). For example, for strain AB00024, the genotype is adeT127::T26, and for strain AB00033, the genotype is ABUW_0020-148::T101.
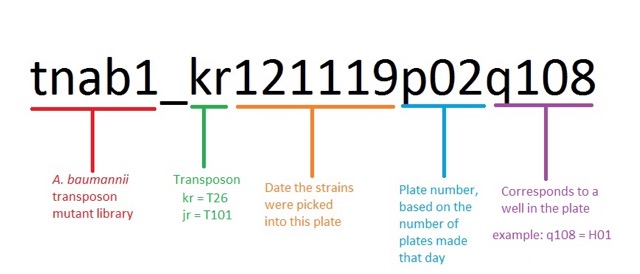
Please follow these links for additional information:
Academic institution order form
Non-academic institution order form
Ab three-allele library